Project Overview
This project is part of a larger institutional initiative at HSUHK that integrates Game-Based Learning and Generative AI into education. Developed collaboratively by the Department of Economics and Finance, Centre for Teaching and Learning, Digital Learning Section, and Centre for Teaching and Learning, Service-Learning Section, the project empowers students to co-design educational games that teach financial literacy to elderly community members.
With Generative AI tools supporting storytelling, design, and reflection, students not only enhanced their creativity but also critically evaluated the ethical implications of AI use.
What We Did
Game Design for Learning
Students crafted engaging, educational games to help elderly participants understand money management and financial choices.
GenAI as Creative and Critical Partner
AI tools like ChatGPT and Suno were used not just for content creation but also to prompt students to question, refine, and take responsibility for their outputs.
Community Engagement
The games were delivered in real-life community workshops, providing students with authentic feedback and an opportunity to reflect on social responsibility.
Reflective Research
Student reflections and evaluation tools captured growth in creativity, ethical reasoning, empathy, and self-efficacy.
Impact Highlights
-
- Over 300+ students involved in this initiative
-
- Enhanced critical thinking, ethical awareness, and collaborative problem-solving
-
- Reached 700+ elderly participants with student-created financial literacy games
-
- Shortlisted in QS Reimagine 2024 (Best Use of Generative AI)
Digital Extensions: MOOC & AI Chatbot
From Concept to Classroom – Educational Game Design with Generative AI

To extend the impact of this initiative beyond the classroom, we are developing a self-paced online course designed for educators and students alike. The MOOC guides learners through the process of designing educational games using Generative AI tools—from storytelling to mechanics and implementation. Participants will explore real-life case studies, gain hands-on experience with AI tools, and reflect on ethical considerations in AI-assisted learning design.
Key Highlights:
-
Designed for beginners with no programming background
-
Integrates practical tools like ChatGPT, Suno, and text-to-image platforms
-
Based on the same game-based learning framework used in FIN1001
-
Emphasises responsible AI use and creativity in education
AI Chatbot: Empowering Orientation and Learning Support
We also developed a customised AI chatbot—trained on HSUHK’s student resources—to support incoming students during New Student Orientation. The chatbot responds to questions in English, Traditional Chinese, and Simplified Chinese, and is capable of handling both button-based and free-text queries. Learning analytics revealed peak usage during late evening hours, proving its value as an always-available student assistant.
Students’ work showcase
Framework & Pedagogical Approach
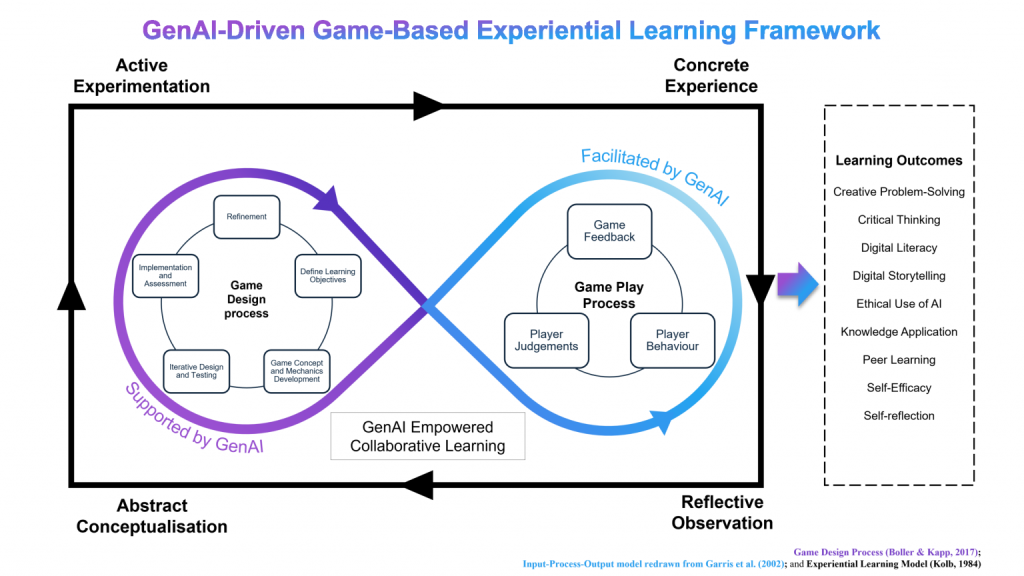
How It Works:
- Game Design Process: Students engage in a creative and iterative cycle where they define learning objectives, develop game concepts, and refine their designs through testing and feedback. Generative AI plays a crucial role in this process by supporting creativity, offering real-time feedback, and facilitating the refinement of ideas.
- Game Play Process: The learning continues as students participate in the games they’ve designed, where they receive immediate feedback, make judgments, and adjust their strategies. AI enhances this process by adapting the gameplay to individual learner needs, ensuring a personalised and immersive experience.
Learning Outcomes:
This framework is built on the foundation of Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle, enhanced by the motivational and engagement principles of Game-Based Learning, and empowered by the capabilities of Generative AI. It seamlessly combines the Game Design Process and the Game Play Process into a cohesive, cyclical model that supports active learning, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
Why It Matters:
The GenAI-Driven Game-Based Experiential Learning Framework represents the future of education, where technology and pedagogy intersect to create powerful learning experiences. By integrating Generative AI into both the design and execution phases of learning, we are able to offer students a truly transformative educational experience that is both engaging and effective.
References:
Boller, S., & Kapp, K. (2017). Play to learn: Everything you need to know about designing effective learning games. Association for talent development.
Garris, R., Ahlers, R., & Driskell, J. E. (2002). Games, Motivation, and Learning: A Research and Practice Model. Simulation & Gaming. 33(4). 441–467.
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Students Voices
Teams & Collaboration
- “By engaging elderly participants through games and videos on personal finance and anti-fraud awareness, students learned the value of patience, cross-generational communication, and the importance of making financial knowledge accessible to all.”
- “Whether designing games or producing educational videos with legal experts, students gained hands-on experience in translating financial and legal concepts into clear, engaging formats—building both their confidence and a sense of purpose beyond the classroom.”
- “While (Gen)AI tools can offer valuable support in generating ideas and questions, their biggest advantage lies in reorganizing information and providing simpler and more concise texts. It is essential to complement their capabilities with human knowledge and judgment.”
- “By creating games with AI to teach elderly people about money, we learned to work as a team, care about real-world problems, and realise that financial planning—and social impact—starts with us.”
Presentations, Publications & Recognitions
Woo, Y. Y., & Wan, K. (2024, August 23). Integrating generative AI into service-learning: Enhancing student learning and financial literacy for the elderly through game-based activities. Paper presented at the 8th International Academic Conference on Education, Oxford, United Kingdom.

Ms Rosalie WOO presented her findings at the 8th International Academic Conference on Education.

Volunteer New Star Award from The Christian Family Service Centre (the community partner) at the Corporate Recognition Ceremony 2024

Ms Rosalie WOO and her students’ sharing at the HSUHK Symposium on Using Generative AI (ChatGPT) for Enhancing Academic Teaching

From left: Dr CHAN Chi Ming, Victor; Ir Dr HO To Sum, George; Dr CHENG Ka Ming, Ben; Ms WOO Yan Yin, Rosalie (Principal Team Leader); Mr WAN Tsz Hin, Kelvin (Co-Team Leader); Ms LEE Ching Ching, Charlotte; and Ms YIP Wai Yee, Waii
Community Partners:
- Evangelical Lutheran Church Social Service Hong Kong Sheen Hok Charitable Foundation Kwan Shon Hing Yu Chui Neighbourhood Elderly Centre (信義會愉翠長者中心)
- Christian Family Service Centre – True Light Villa District Elderly Community Centre (CFSC真光苑長者地區中心)
- Christian Family Service Centre – Shun On District Elderly Community Centre (CFSC順安長者地區中心)
- HKSKH Kei Oi Neighbourhood Elderly Centre (基愛長者鄰舍中心)
- Sik Sik Yuen Ho Tai Neighbourhood Centre for Senior Citizens (嗇色園主辦可泰耆英鄰舍中心)
